
Please contact email protected to delete if infringement. (dfcdf <- transform(df, p cumsum(p)), type 'l') points(dfcdf) Collected from the Internet. After quantization, if PMF does not sum to 2precision, then some values of PMF are increased or decreased to adjust the sum to equal to 2precision. No distribution is specified so I cant use the build in commands. For discrete random variable that takes on discrete values, is it common to defined Probability Mass Function.
#Pmf to cdf pdf
The PDF (defined for Continuous Random Variables) is given by taking the first derivate of CDF. The reader is encouraged to verify these properties hold for the cdf derived in Example 3.2.4 and to provide an intuitive explanation (or formal explanation using the axioms of probability and the properties of pmf's) for why these properties hold for cdf's in general. For entropy encoders and decoders to have the same quantized CDF on different platforms, the quantized CDF should be produced once and saved, then the saved quantized CDF should be used everywhere. Its more common deal with Probability Density Function (PDF)/Probability Mass Function (PMF) than CDF.
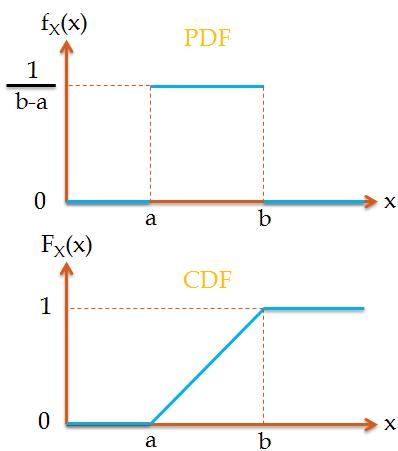
We end this section with a statement of the properties of cdf's. The pmf for any discrete random variable can be obtained from the cdf in this manner. Great share Did notice that the output for BIAS looks like the 95 point interval for the FAIR flip distribution within the graph. Additionally, the value of the cdf for a discrete random variable will always "jump" at the possible values of the random variable, and the size of the "jump" is given by the value of the pmf at that possible value of the random variable. 1 thought on Binomial CDF and PMF values in R (and some plotting fun: overlapping semi-transparent histograms) Anonymous at 4:09 pm.

This is the case for all discrete random variables.
#Pmf to cdf series
Note that the cdf we found in Example 3.2.4 is a "step function", since its graph resembles a series of steps. The reader is encouraged to verify these properties hold for the cdf derived in Example 3.2.4 and to provide an intuitive explanation (or formal explanation using the axioms of probability and. Express the PMF as follows, p ( x) ( 0.4) ( x 1) + ( 0.3) ( x 2) + ( 0.2) ( x 3) + ( 0.1) ( x 4) The CDF is then given by integration, by definition, if P ( x) is the CDF then, P ( x) x p ( y) d y Observe that if x < 1 then each of the delta functions vanish and so P ( x) 0. We end this section with a statement of the properties of cdf's. You can compute the CDF using delta-functions. \(X\sim Bin(39,0.25)\).Then sample 999 random binomials with 39 trials and probability of success 0.25 and plot them on a histogram with the true probability mass function. To summarize Example 3.2.4, we write the cdf \(F\) as a piecewise function and Figure 2 gives its graph: The pmf for any discrete random variable can be obtained from the cdf in this manner. Plot the pmf and cdf function for the binomial distribution with probability of success 0.25 and 39 trials, i.e. Calculate mean and variance of the distribution.' I obtained 51356 males and 48644 females, a difference of 56. \(F(18) = P(X\leq18) = P(X\leq 2) = 1\) Draw the PMF and the CDF of the probability function of this experiment (on a sample of 50 births).

The joint cumulative distribution function of two random variables $X$ and $Y$ is defined as


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
